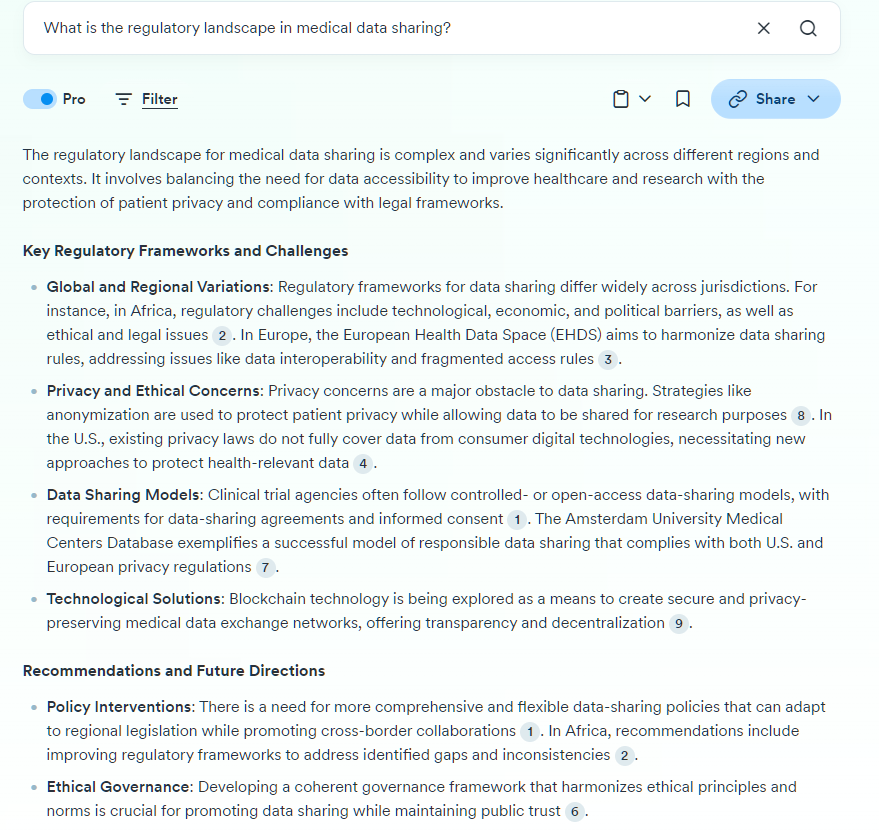
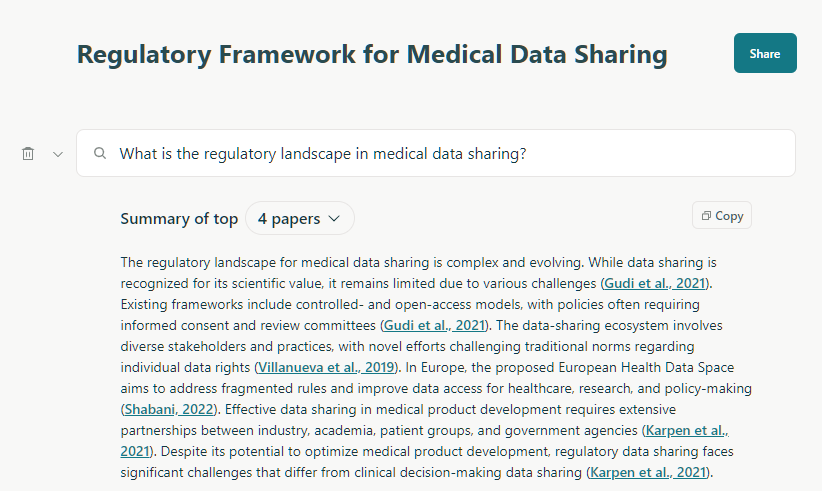
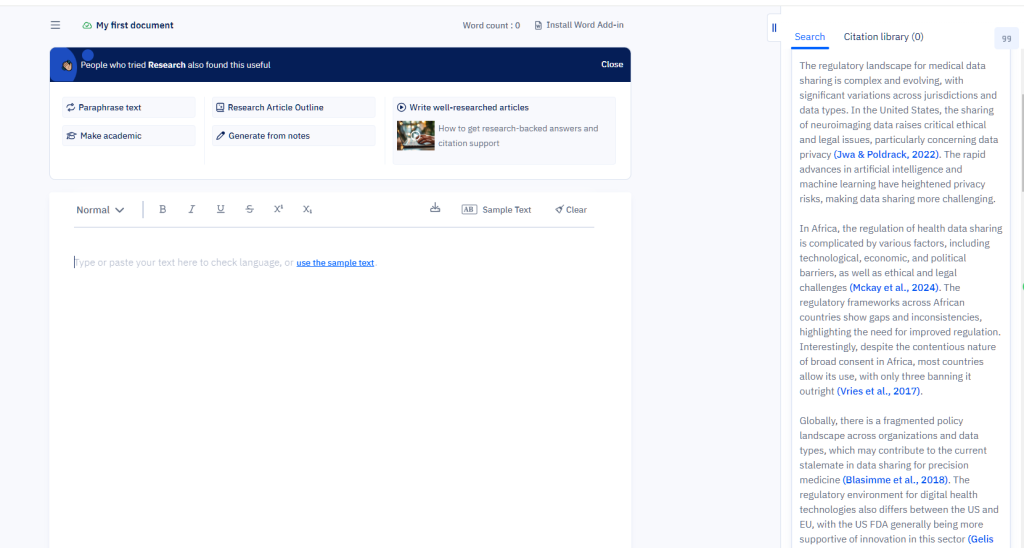
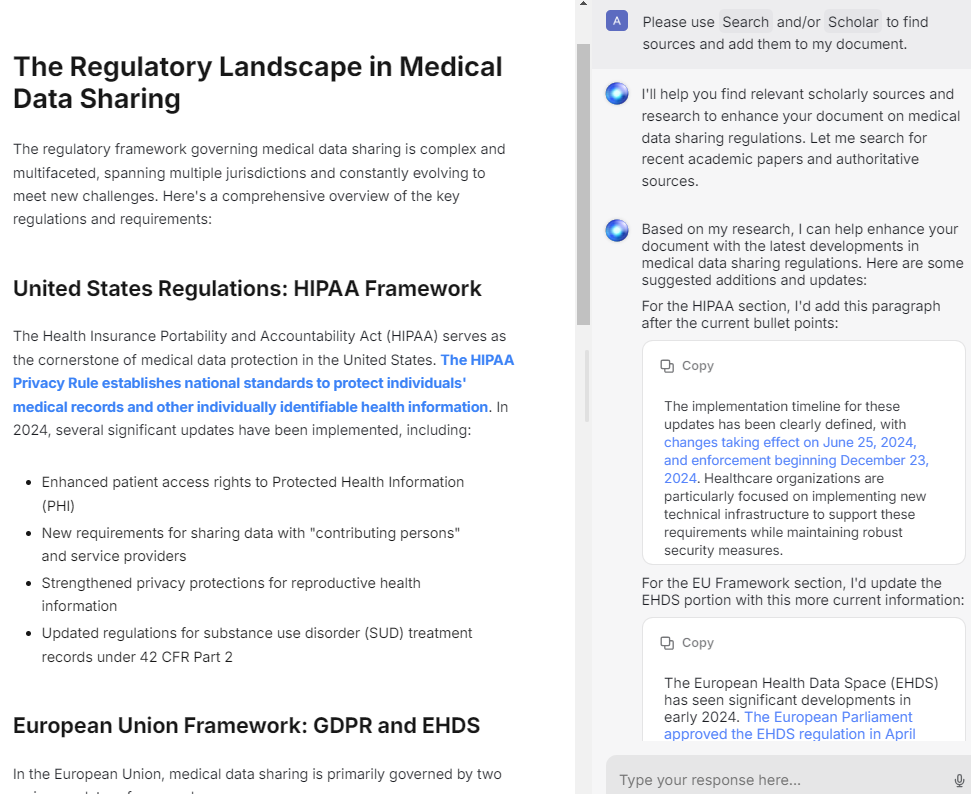
I recently completed with the help of Claude – an interactive visualization of moving dots that form different geometric patterns. What makes this particularly satisfying is that I managed to create it mostly through vibe coding.
The Inspiration
I first came across this mesmerizing pattern a few years ago and could not anymore find the original source. Reverse google search though revealed it was also on Reddit.
I wanted to recreate ifor my class. I wanted to make my students guess the underlying patterns as these dots moved. When I teach, I teach mostly through frameworks – always insisting to my students that different people can interpret the same events differently because of their varying perspectives. Depending on which patterns you focus on, you see completely different shapes emerging from the same moving dots.
Vibe Coding with Claude
Starting with just a basic concept, I asked Claude to help me build a heptagram. I asked it then to find 4 triangles with the same dimensions with the vertices along the perimeter of the heptagram. For the longest time, it seemed impossible. I kept tweaking my prompts, explaining what I wanted, but couldn’t quite get there.
I then changed my approach, prompting about dots moving along its perimeter. The initial implementation was straightforward. To help me make sense of it, I asked Claude to implement controls for:
- Adjusting the number of dots
- Changing their speed
- Allowing users to connect dots to form shapes
The real challenge came when I wanted to add triangles and squares that would be overlaid as the dots moved. The first breakthrough came when I realized we needed to treat the heptagram as if it were a flat line with dots spaced proportionally along it. The triangles emerged but they did not look good. At first, the triangles formed by the dots would constantly change size, which wasn’t what I wanted.
After much experimentation, the second breakthrough came when I realized that the key was having the dots slow down near the vertices of the heptagra.
The Result
What you see now is a fully interactive visualization that my students can explore. They can experiment with different settings, observe how the patterns form and transform, and develop their intuition about multiple perspectives. It beautifully illustrates how the same underlying data can yield different interpretations depending on what you choose to focus on.
Despite having no coding background, I was able to recreate a complex mathematical visualization that I can now use in my classroom.
Vibe coding is really becoming a thing.
There's a new kind of coding I call "vibe coding", where you fully give in to the vibes, embrace exponentials, and forget that the code even exists. It's possible because the LLMs (e.g. Cursor Composer w Sonnet) are getting too good. Also I just talk to Composer with SuperWhisper…
— Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy) February 2, 2025